Procurement is vital for any organization, ensuring that goods and services are acquired efficiently, cost-effectively, and ethically. But the procurement process can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those new to the field.
That's why we've compiled this comprehensive guide to understanding the procurement lifecycle in 15 easy steps. From identifying procurement needs to contract closeout, we'll take you through each process stage and provide practical tips and strategies to help you succeed.
Whether you're a professional or just starting, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills you need to confidently navigate the procurement lifecycle.
The procurement life cycle for a business involves various steps in acquiring goods or services. To attain an efficient procurement life cycle, procurement management strives to optimize speed and cost-effectiveness in its design. By achieving this efficiency, the procurement process can obtain essential goods and services quickly, thus lowering costs. Furthermore, companies that competently manage their procurement life cycle can enhance customer relationships by ensuring dependable product delivery.
When procuring goods and services, businesses often require a wide range of items, from essential manufacturing equipment to daily supplied needed at office and consulting services.
The procurement can be divided into the following groups:
1. Direct Procurement
Direct Procurement involves acquiring goods or materials essential for producing a company's products and directly impacting its profitability. These include all raw materials required for production, like silicon wafers for semiconductor firms, and products for resale. Direct Procurement also covers the purchase of machinery or technologies utilized to develop a company's goods or services, like robots in an automobile factory.
2. Indirect Procurement
Regarding Procurement, Indirect Procurement pertains to acquiring goods or services that are vital to a company's everyday operations but do not directly add to its revenue. These expenses include maintenance fees, office overheads, and travel expenses, which can affect a company's profitability. This underscores the significance of an effective life cycle for indirect Procurement.
3. Service Procurement
Service Procurement encompasses procuring services that vary from third-party contact centers to on-site contingent labor or security services to obtain people-based services. Examples include bringing on an implementation partner to help deploy a new ERP platform or hiring an individual with the expertise required to tackle a significant business challenge. It's essential to note that Service Procurement can include both Direct and Indirect Procurement.
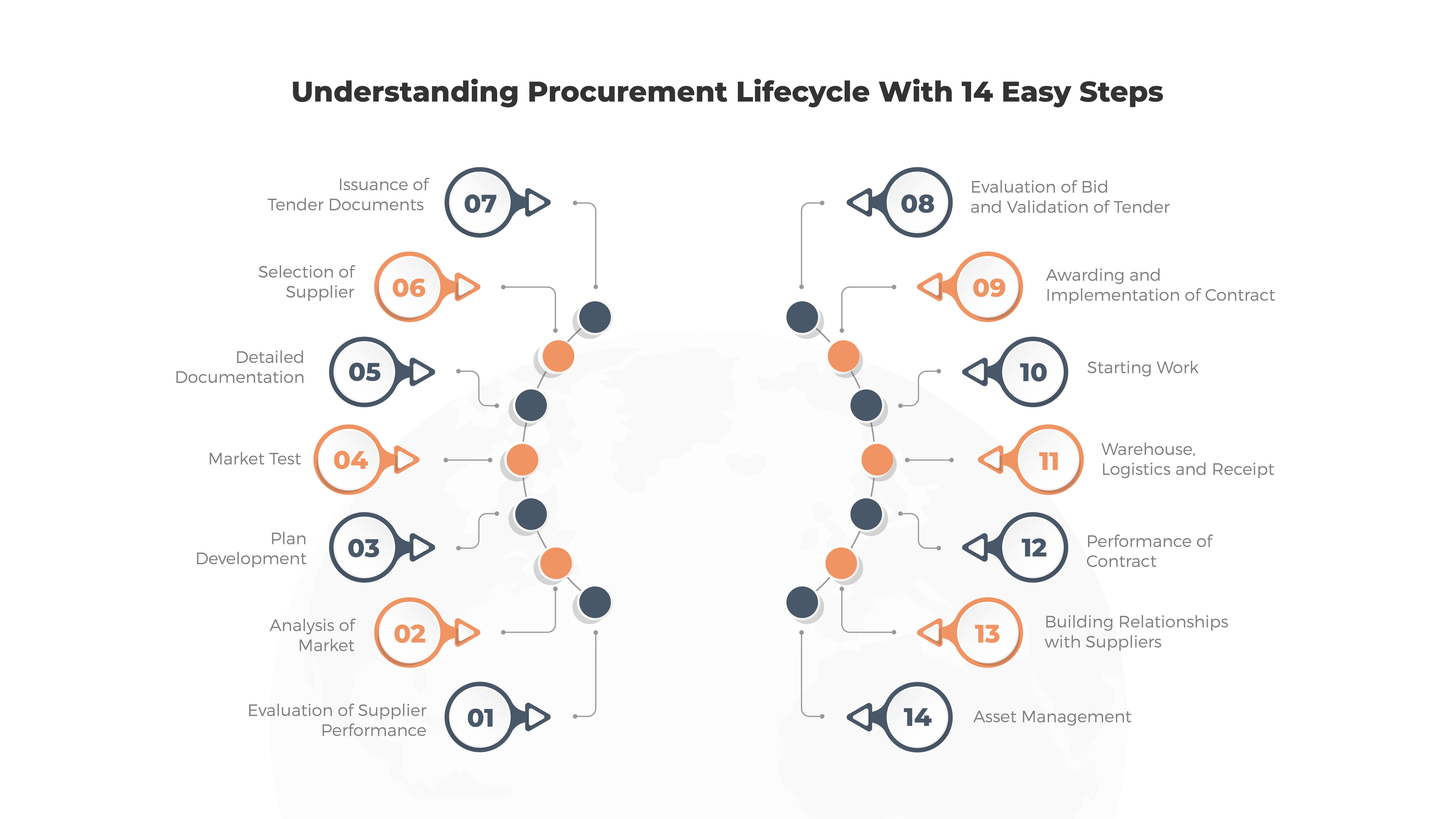
The procurement life cycle encompasses various steps that may differ across companies and industries, but many remain consistent. As a company builds a trusted network of suppliers, it may reduce the required steps, eliminating some tendering and supplier validation processes.
The following are 14 crucial stages of the procurement life cycle.
1. Defining Your Business Needs
To effectively meet your company's needs, defining clear criteria is crucial. This requires involving multiple stakeholders in the procurement life cycle, from employees initiating requests to those responsible for supplier selection. For instance, a growing business may need a new technology provider to support increasingly complex requirements or to source new raw materials and machinery to launch a product line.
2. Analysis of Market
The next step is conducting market research to make informed decisions considering your current position and market conditions. After analyzing the market, you can weigh the options and decide whether to outsource or manufacture the product.
3. Plan Development
A solid plan that considers the effects of the external environment must be developed after conducting a thorough market analysis and understanding the dynamic market conditions. It would be advantageous to submit competitive procurement offers if you can outperform the other players in your market by offering a superior product that distinguishes you from the competition. If you only have one supplier, it might be more efficient to increase market competition or bring procurement in-house.
4. Market Test
The specific requirements of all stakeholders as well as the needs of the business as a whole must be considered when deciding on the procurement strategy. You can then evaluate how easily the procurement strategy can be modified to meet those needs.
Such a market test will help determine when it is best to enter the market or if it would be better to hold off.
5. Detailed Documentation
To minimize the adverse financial impact of incorrect specifications, producing thorough and pertinent documentation encompassing a comprehensive breakdown of the service level agreements, terms and conditions, and volume details is crucial. Such a detailed breakdown guarantees consistency in pricing, product quality, and operational functionality.
6. Selection of Supplier
Upon completion of the review of RFI responses, it is possible to generate a list of suppliers that fulfill the criteria. Some entities may perform an initial supplier ranking based on their abilities at this stage. When developing the list, it is essential to consider both present and future needs, as the chosen suppliers could turn into long-term collaborators. To establish a robust and beneficial partnership, prioritize selecting accountable and dependable partners who communicate effectively and meet the technical prerequisites.
7. Issuance of Tender Documents
Upon identifying the suitable companies for participation, the selected suppliers must issue formal documentation, including an Invitation to Tender (ITT) and a Request for Quotation (RFQ). It is compulsory to provide extensive documentation detailing the business requirements and a definite response timeframe.
8. Evaluation of Bid and Validation of Tender
After receiving and reviewing the submitted tenders, the subsequent phase is assessing and validating the bids against predetermined award criteria. The goal is to determine which offer provides the best value for money (VFM) and select the most suitable supplier based on these factors. Conducting a rigorous and well-organized tender evaluation that is transparent, systematic, and includes comparisons of prices and technical aspects is crucial.
9. Awarding and Implementation of Contract
The contract will be awarded upon choosing the preferred supplier, outlining the respective duties, responsibilities, and essential success criteria for both parties. This agreement establishes a solid groundwork for managing the contract and the partnership efficiently and effectively.
10. Starting Work
After signing the contract, the supplier commences work by manufacturing and delivering the goods or services as stipulated in the agreement. This process continues until the completion of the contract.
11. Warehouse, Logistics and Receipt
Once the supply contract becomes binding, the vendor assumes responsibility for providing the supplies as requested by the customer, adhering to the specifications agreed upon during the contract award phase. Logistics and warehousing agreements made earlier play a critical role in ensuring supply deliveries' seamless and efficient management. This encompasses aspects such as product coding and classification, spacing, layout, racking, and the frequency of delivery as agreed upon.
12. Performance of Contract
It is essential to monitor the performance of the contract regularly and assess it at designated intervals against the key performance indicators agreed upon in the agreement. This assessment should also encompass discussions on the effectiveness of the relationship, identifying and resolving any conflicts or issues utilizing the agreed-upon procedures and timeframe. Additionally, exploring opportunities for continuous improvement and establishing the next review date is advisable.
13. Building Relationships with Suppliers
Effective management of supplier relationship forms an integral component of supply chain management (SCM), involving regularly reviewing suppliers to determine the appropriate level of collaboration and effort required to foster a constructive partnership and achieve specific objectives. By establishing the proper relationships and environment, innovation and development can be facilitated, leading to a faster and more efficient process.
14. Asset Management
Due to various factors, such as shifting focus, and exploring new niches within the industry. By modifying the product line, your organization's requirements may evolve. Therefore, it is vital to conduct periodic evaluations of your procurement needs to assess any changes and identify how you can modify your procurement approach accordingly. Asset management entails keeping track of your procurement requirements to ensure that the procurement process aligns with and supports your business operations effectively.
For any organization, managing suppliers is a critical process that involves various activities, such as supplier selection, contract negotiation, performance monitoring, and issue resolution. However, despite its significance, many organizations require assistance in supplier management.
The following are some challenges they may face:
● Supplier selection: With limited information and numerous potential suppliers, identifying and choosing the right supplier can take time and effort.
● Contract negotiation: Creating a fair and sustainable agreement requires a balance of both the organization's and supplier's needs, which can be challenging.
● Supplier performance monitoring: Tracking supplier performance, particularly with multiple suppliers and a high volume of transactions, can be daunting.
● Communication and collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration with suppliers are essential to ensure their understanding of the organization's requirements and expectations.
● Risk management: Managing supplier risks, such as supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and compliance risks, necessitates a robust risk management process.
● Data management: Managing supplier-related data, including contracts, performance metrics, and compliance documentation, can be complex and requires dependable data management systems to ensure accuracy and accessibility.
● Cultural differences: Working with suppliers from different countries requires sensitivity to cultural differences, language barriers, and varying business practices.
TWhen it comes to the early stages of procurement, where multiple stakeholders need to validate business needs, things can quickly become chaotic. But, we've got you covered with five best practices to optimize your procurement life cycle!
If you want to avoid supply delays, additional operating costs, and endangered relationships with vital suppliers, which may hinder your ability to serve customers, it's crucial to have proper management. Therefore, you must keep the procurement juggling act from spiraling out of control.
Here are five ways to optimize your procurement lifecycle:
● Optimization of Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is essential to purchasing new supplies at the right time. Many companies rely on cloud-based inventory management systems to balance inventory capacity and costs. By using inventory management systems, businesses can obtain real-time insights into their inventory levels, predict future needs, and alert purchasing supervisors when it's time to restock shelves.
● Mastering Transparency: When faced with issues like distribution network slowdowns, companies may need to change their plans significantly. In such circumstances, visibility and transparency are crucial to effectively managing the procurement life cycle. If all stakeholders can access information and reports throughout the procurement process, they will be better equipped to perform their duties and handle any last-minute modifications.
● Beneficial Supplier Relationships: The best type of supplier relationship is one that benefits both parties. It provides a dependable partner for your company to obtain necessary goods and services while offering your supplier a steady source of income and a chance to expand their business with a case study.
Effective communication is a natural byproduct of a healthy relationship. For example, it is always recommended to notify suppliers of potential future risks, to prepare them for any crisis. In return, transparent suppliers prevent your business to avoid shortages by communicating any delivery-related issues that may arise.
● Structured Procedure: For a procurement life cycle to be efficient, it requires a strong foundational structure. Defining the best practices, assigning clear ownership, and detailing each step can all help ensure the smooth operation of the procurement process.
● Automation of Administrative Tasks: Dealing with market fluctuations while managing procurement manually can be a daunting task. One way to alleviate this burden is by incorporating automation in various elements of the procurement life cycle. Automating invoice payments and reordering, as well as the approval process can lead to high cost and time savings and reduces the risk of human error.
BusinessBid's procurement management system allows you to exercise complete control over your business effectively managing procurement processes and supply chains effectively. Using BusinessBid, you can easily record and update real-time production data, financial reports, inventory, and outstanding orders.
With BusinessBid, your critical supply chain management systems operate on the same updated information, ensuring that your procurement processes are coordinated and automated. You can also forecast demand accurately and reduce administrative tasks significantly.
So why wait any longer? Take advantage of BusinessBid's procurement management system today and streamline your procurement processes for optimal efficiency and productivity. Visit the website now for details!