As a smart business owner, it is crucial to understand the role of cash outflow as a vital component of financial success.
More than simply making purchases and hoping for the best - your business must actively plan, manage, and monitor its expenditures. If you fail to do so, it can significantly impact your profit margin.
It may be difficult to distinguish between invoices and purchase orders, especially if you are new to the procurement process. This issue is not limited to new members, as even procurement team members may have varying perspectives and definitions regarding these terms.
Understanding these basic procurement terms could prevent you from overlooking critical financial documents, potentially negatively impacting organizational spending. Therefore, it's crucial to have a basic understanding of the procurement process.
When it comes to running a business, managing finances is a crucial aspect that can make or break the success of the company. One of the key components of financial management is managing purchase orders and invoices.
Purchase orders and invoices serve as the backbone of any transaction. In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of purchase orders and invoices, exploring their importance, the differences and similarities between the two, and best practices for managing them effectively.
Whether you are a seasoned business owner or just starting out, understanding the ins and outs of purchase orders and invoices is essential for the financial health and growth of your business, and this guide will surely help you to do so.
A purchase order (also known as PO) is a document issued by a buyer to a supplier, specifying the details of the goods or services he intends to purchase. It is a formal agreement between the two parties that outlines the terms and conditions of the transaction.
It serves as a legally binding contract between the two parties and is used as a reference by the supplier to prepare and deliver the goods or services.
Once the supplier receives the purchase order, they typically review the details and send an order confirmation to the buyer. This helps ensure that both parties agree on the details of the transaction and can proceed with the order fulfillment process.
When the company can receive early volume discounts for all orders from a vendor within a specific time frame, a blanket purchase order may be issued.
Subsequently, the company releases underlying sub-purchase orders periodically to request goods from the vendor under the large blanket purchase order.
In the case of office supplies not purchased in bulk, a business may opt not to prepare a purchase order due to the relatively high procurement costs associated with creating them compared to the item's price.
However, purchase orders can be useful for various purposes, such as budget management, preventing duplicate orders, inventory monitoring, making strategic purchase decisions, and price negotiation.
The purchase order typically includes information such as the product or service description, quantity, price, delivery date, and settlement terms.
Here are the elements of a purchase order:
● Product/service description: Generally, the item you requested is the item you will receive. Hence, the purchase order's item description must specify the item requested by the ordering department.
● Quantity: Although this may appear straightforward, many erroneous orders occur due to inaccuracies in quantities and units. To avoid such errors, determine the required number of items. Make sure to determine the correct required quantity in order to avoid any future discrepancies.
● Price: Once more, a seemingly uncomplicated aspect; however, various factors must be considered when establishing the price. For instance, the unit used to quote the price must be determined, such as per piece, per package, per ton, or another functional unit. It is essential to establish whether the price includes shipping and handling costs.
● Delivery date: The buyer should specify a certain date as to when he wishes to receive the shipment, or else late delivery could delay the production process. During price negotiations, the buyer should inform the seller of the expected delivery date.
● Settlement terms: The buyer can utilize settlement terms to save their agency money, even though this element is often disregarded. "Payment/Settlement terms" refer to the seller's expected payment schedule and whether they offer early payment discounts.
An invoice is a document that represents a payment request and serves as a physical record of a transaction between a buyer and a vendor. The status of an invoice can be "open" if it is awaiting payment from the customer or "paid" if the customer pays immediately, either in-store or through online e-commerce.
In the case of a credit sale, the vendor typically creates an invoice and sends it to the buyer after completing the sales transaction. The invoice lists the goods or services provided and the total amount due. The seller may also include details of their preferred payment options, such as cheque, cash, or electronic payment.
In addition to its role as a payment request and record, an invoice can serve as a legal document and be used as evidence in case of a breach of rights.
Your business can also benefit from record-keeping, payment tracking, easy tax filing, and the ability to identify customer buying patterns and trends.
All elements in an invoice help the seller ensure that the buyer has all the information they need to make a payment and address any questions or concerns that may arise.
Additionally, a well-crafted invoice can help to avoid disputes or legal issues down the line. Here are some of the key elements that a good, legally-sound invoice should contain:
● Invoice number: A unique identifier that helps the buyer and seller track the transaction.
● Date: The date the invoice was issued is important for record-keeping and tracking payment due dates.
● Contact details: The seller and buyer's name, address, and contact information.
● Description of goods or services: A detailed list of the goods or services provided, including quantities, unit prices, and total prices.
● Payment terms: The payment terms agreed upon by the buyer and the seller, including the due date and any late payment fees or discounts for early payment.
● Total amount due: The amount due for the goods or services provided, including applicable taxes or fees.
● Payment options: The payment methods the seller accepts, such as cheque, cash, or electronic payment, along with any relevant details or instructions.
● Terms and conditions: Any additional terms and conditions that apply to the transaction, such as warranties, return policies, or dispute resolution processes.
● Signature and date: The seller's signature and the date the invoice was issued can serve as proof of the transaction.
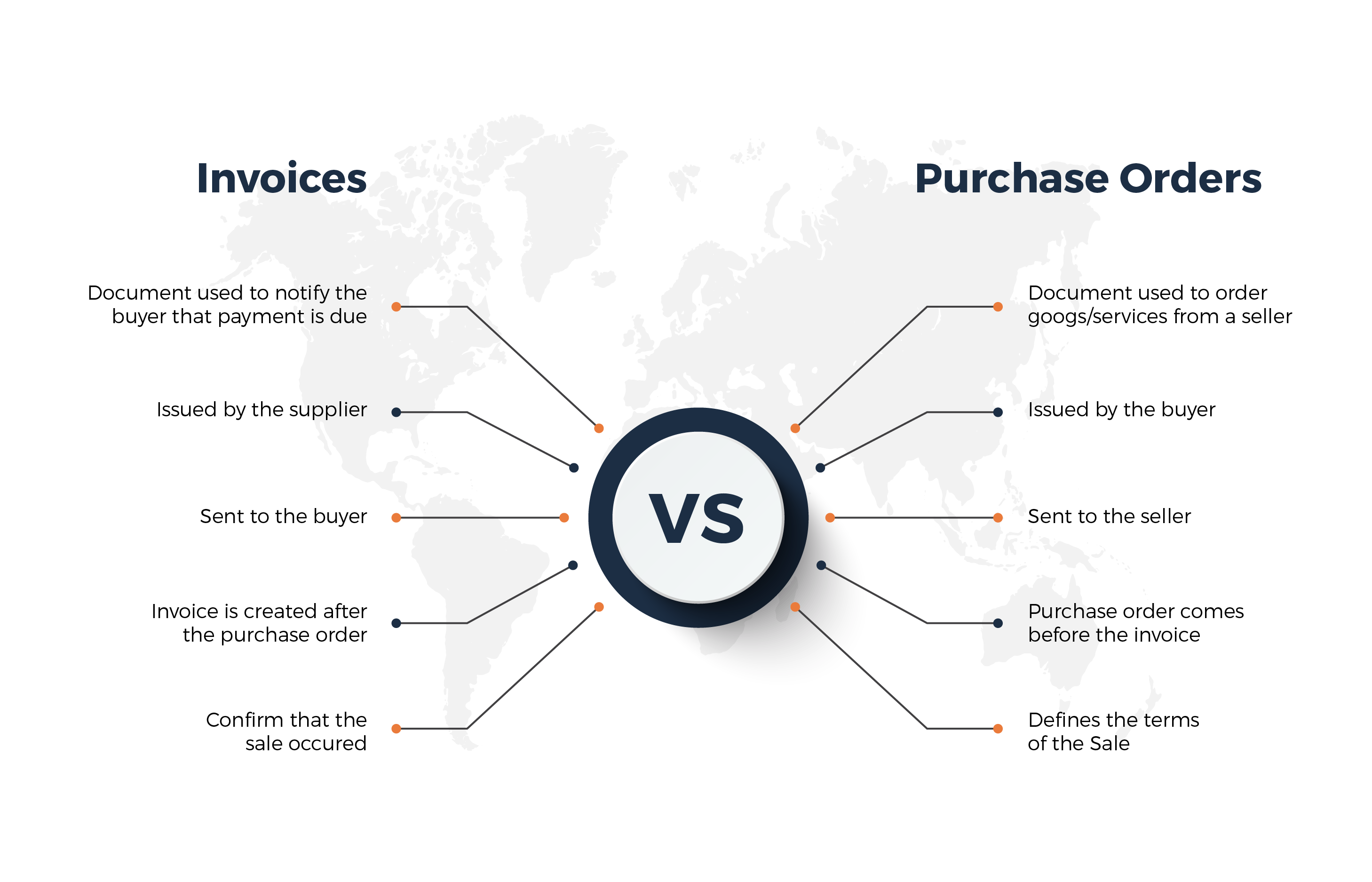
Although a purchase order and invoice may appear similar, they have significant differences. Here are a few distinctions:
1. A purchase order is usually one of the initial stages in formalizing a purchase or business transaction for a product or service.
An invoice is generally issued when the sale is complete, and payment is due.
2. The buyer sends a PO to the supplier to establish a contract between the parties.
The vendor provides invoices to the purchaser, which are sent at the end of the transaction based on the information from the purchase order and payment terms.
3. An invoice is assigned an invoice number. Employing a numbering system is critical for generating unique codes to prevent accounting errors and duplications, which are referenced throughout the transaction process.
The procurement department assigns PO unique PO IDs.
4. Last but not least, the information provided can differ. For instance, a purchase order typically includes a comprehensive description of the order, including brand names or catalog numbers, delivery date and location, and payment terms.
In contrast, an invoice usually contains the purchase order and invoice numbers and an itemized breakdown of the order's cost.
A purchase order often contains more specifics on how and when the vendor can process and deliver an order, while an invoice generally includes more information on payment terms.
Although purchase orders and invoices have distinct differences, they also share several similarities as they are both types of commercial communication used in purchases.
Many businesses regularly utilize purchase orders and invoices as integral parts of their procurement operations.
● Both may pertain to the same goods or services and often include comparable information about the buyer and vendor.
● They serve as legally binding documents between the buyer and the vendor, and companies frequently use both as communication tools during business transactions.
● PO and Invoices can aid businesses in effectively tracking and managing their inventory by serving as evidence for financial audits and forming the basis for a company's financial statements.
● They contribute to effective financial management.
Invoices can follow from a purchase order once it is complete but can also be issued without a previous purchase order.
The purchase order serves as a form of pre-approval for an order, which can help resolve any issues that may arise with the order or payment terms at a later stage.
Nonetheless, a purchase order cannot be considered an official request for payment, as an invoice must be issued for this purpose.
Companies require both purchase orders and invoices for several reasons.
1. Purchase orders help establish a clear and formal agreement between the buyer and seller about what goods or services are being purchased, at what price, and under what terms and conditions. This helps avoid confusion and misunderstandings during the procurement process.
2. Purchase orders can help companies manage their inventory by providing a detailed record of the products or services ordered, the quantities, and the delivery date.
This information can be used to track inventory levels and ensure that the company has the necessary supplies to meet customer demand.
3. Invoices serve as formal requests for payment from the seller to the buyer after the goods or services have been delivered or completed.
Invoices typically include detailed information about the products or services provided, the price, and the payment terms. This helps ensure that the buyer pays the correct amount and is on time.
4. Finally, purchase orders and invoices serve as important financial records for the company. They provide evidence of transactions and form the basis for financial reporting, budgeting, and forecasting.
They also help companies track their expenses and income, essential for effective financial management.
Companies require purchase orders and invoices to establish clear agreements, manage inventory, request and process payments, and maintain accurate financial records.
Digitization has become crucial for businesses adapting to the digital era.
It is worth prioritizing electronic procurement as part of the digital transformation strategy, enhancing supplier relationships, automating orders and procurement procedures, and improving spending transparency.
Automating and digitizing the procurement process involves utilizing digital tools and leveraging the process data intelligently for better decision-making. This will lead to a more efficient and accurate outcome.
There are numerous advantages to implementing digital systems for managing purchase orders and invoices, including:
● Streamlining the process to make it quicker and more accurate, reducing errors and saving time.
● Providing real-time tracking and monitoring of purchases and payments, improving accountability and transparency.
● Reducing costs associated with paper-based systems, such as printing, mailing, and storage.
● Integrating with other business software, such as accounting and inventory management, provides a comprehensive business operations solution.
● Enhancing security and data privacy, reducing the risk of fraud, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Digitalizing purchase orders and invoice management can significantly benefit businesses, making the process more efficient, effective, and secure.
To wrap it up, purchase orders and invoices are vital documents that can significantly benefit small businesses. They can help maintain accurate financial records, streamline processes, facilitate payments and collections, and provide a clear paper trail for auditing purposes.
Whether you choose to stick to traditional paper-based methods or embrace digital solutions, implementing a system for purchase orders and invoices can ultimately save time, reduce errors, and improve your overall financial management.
By using these documents effectively, businesses can ensure they stay on top of their finances and achieve long-term success.